Game Changer or Productivity Myth?

The impact of Generative AI on business process automation
1. Can Generative AI finally deliver on its promises?
For years, we’ve been promised that Artificial Intelligence (AI) would change the world, making offices a better place. Only the crypto boom of 2021 managed to overshadow the AI hype. Fueled by recent advancements in Generative AI (GenAI), 2024 is once again buzzing with superlatives. But can GenAI finally deliver on the long-awaited promises to corporates and SMEs?
Human labor is expensive, and onboarding takes time. So far, advanced automation beyond Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has been hampered by the complexity and engineering effort of AI systems. It was easier to hire people than to deploy AI systems. However, the shortage of skilled workers is driving the need for technological solutions, and Gen Z and Millennials expect the same digital convenience in the workplace as on their private mobiles.
2. The next evolution of business process efficiency
To analyze the potential of GenAI for enhancing process efficiency, employee productivity, and cost reduction, we have analyzed nearshore and offshore Shared Service Centers (SSC) as well as Global Business Services (GBS) in close cooperation with students of Duke University over the past few months. Our aim was to confirm our hypothesis that the use of AI for business process automation, data-driven decision taking and augmented knowledge work is a top priority in 2024 and also worthwhile in extremely efficient and effective business processes.
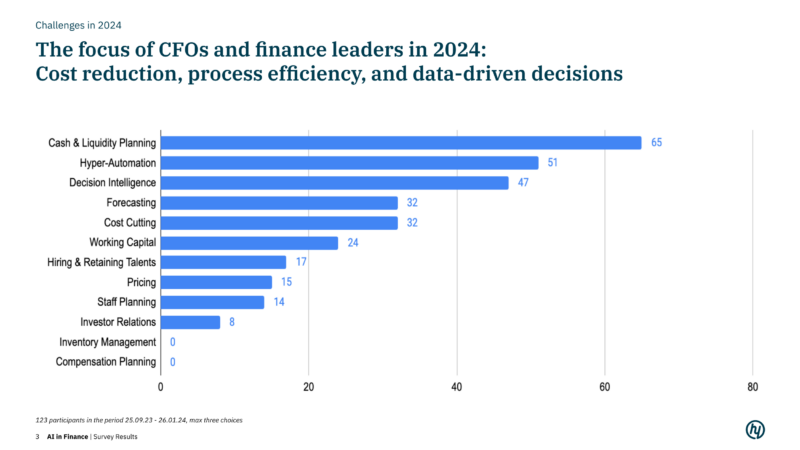
We learnt from 123 survey responses by CFOs, finance directors and leadership teams of SSCs as well as GBSs, that their area of accountability has evolved over recent years significantly. They deepened its functions, broadened its range of services, implemented end-to-end journeys across various processes such as Order-to-Cash (O2C), Procure-to-Pay (P2P), Record-to-Report (R2R), and Hire-to-Retire (H2R), and integrated transversal capabilities like lean management, operational excellence, digital tools, and analytics. Their journey began with labor arbitrage, progressed through improvements in labor efficiency, and leveraged benchmarks for process and operational excellence to surpass peers and provide strategic value.
We have observed that the advent of GenAI is now redefining value creation for corporates and SMEs shifting from a people-driven global enterprise to a generative AI-first enterprise. Started with Intelligent Document Processing (IDP), process mining and narrow AI use cases (“Machine Learning”), today, GenAI is expanding automation beyond traditional, rule-based tasks to more complex tasks with autonomous exception handling and has already shown the capability to generate human-like reports, create visual analytics and slides even in complex corporate domains reducing training and testing efforts at the same time.
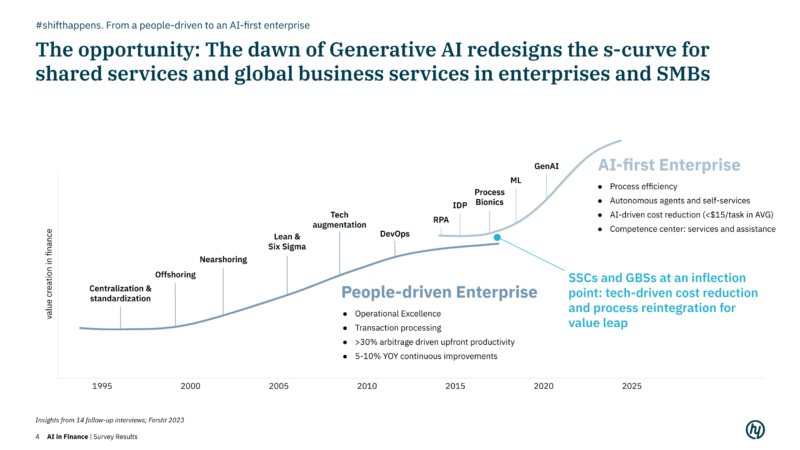
Based on our lessons learnt we defined predictions on how we see the AI automation space evolving:
- Everyone will use an AI assistant: AI assistants will become ubiquitous, augmenting everyone side-by-side from knowledge workers to SSC/GBS agents. This shift will blur traditional lines between vertical applications, automation platforms, and IT services. AI assistants will take various forms, including copilots by incumbents, CRM and ERP systems with complemented AI features, and standalone AI agents.
- Companies will tend to re-integrate: GenAI will become central to automation strategies minimizing the human factor and thus reducing the costs per tasks in SSCs and GBSs under $15. A strong inhouse business case for AI automation of general and administrative tasks is emerging.
- Data, data, data:Investment will focus on machine Learning operations (MLOps) and data orchestration platforms to streamline AI deployment and management.
- Model proliferation: Companies will adopt AI models tailored to specific industries, domains or tasks, leveraging proprietary data to offer superior performance.
- Enhanced user experiences: AI agents will revolutionize customer and employee services by providing personalized, automated interactions. Increased trust in and explainability of fully autonomous AI systems are partially replacing the human in the loop and side-by-side assistants as the preferred solutions even in complex workflows.
3. AI Automation Categories
-
To fully understand the today’s landscape of AI in automation, it is essential to categorize the different types of GenAI tools and their applications:
- Chatbots are one of the earliest and most widespread GenAI applications these days, often utilizing Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems that connect to proprietary knowledge bases for accurate and contextually relevant responses. They handle basic inquiries, provide easy access to policies and procedures, and allow accounting as well as tax self-services.
- AI Assistants surpass chatbots by actively learning user preferences, and performing even complex tasks side-by-side with a human expert in the loop. In corporate settings, they enhance employee productivity supporting experts with data analysis and visualization, generation and validation of management reports and financial statements, forecasting and recommendations on ensuring compliance in accounting-related processes.
- AI Agents represent a more advanced form of automation, capable of handling complex tasks autonomously without any major labeling or training effort. These agents can process large volumes of data, make decisions, and execute actions. They are used in areas such as automated accounting, invoice and payment processing, tax calculations and declarations, leaving only complex cases and exception handling to human experts.
- Agent-to-Agent Automation involves multiple autonomous AI agents working together, interacting and collaborating to complete complex tasks. An Agent-to-Agent Communication Protocol (AACP) enables these agents to share data, assign tasks, and coordinate actions across multiple tasks, workflows or end-to-end processes in O2C, P2P and R2R enhancing overall process efficiency.
4. AI automation is a hard challenge
GenAI is poised to revolutionize automation by enabling businesses to handle complex tasks more efficiently. By focusing on domain-specific models, investing in data infrastructure as well as data governance, companies can harness the full potential of human and machine intelligence.
But, most GenAI use cases are currently in the experimentation or early production stages, focusing on advisory and assistant-oriented workflows. Today, the vast majority of these GenAI systems are not yet capable of predictable planning or reasoning, and areas like memory and context are still under research. AI Automation is a complex and often underestimated challenge.
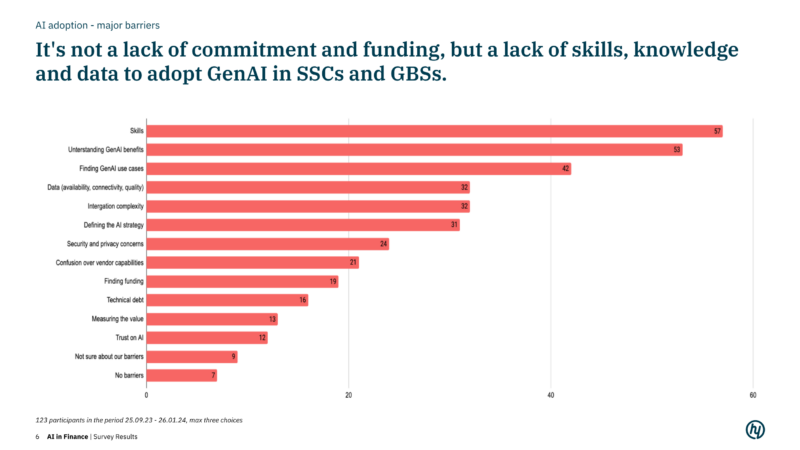
Only 40% of the 123 respondents stated that they have already set up their own AI teams and have predominantly sourced external AI solutions. Companies tend to buy AI systems, in-house development currently plays a subordinate role. This is presumably also because many companies currently lack the skills, knowledge and data to implement GenAI and start with AI use cases that matter most.
To learn more about our research results, GenAI use cases for business process automation, and how you can activate and train your employees getting started with GenAI, please get in touch.


